Rashes are a common skin condition that can affect anyone at any age. They manifest as changes in skin color, texture, or appearance and can be localized or widespread. Rashes can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, and chronic skin conditions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and treating rashes, ensuring you can manage this condition effectively.
Types of Rashes
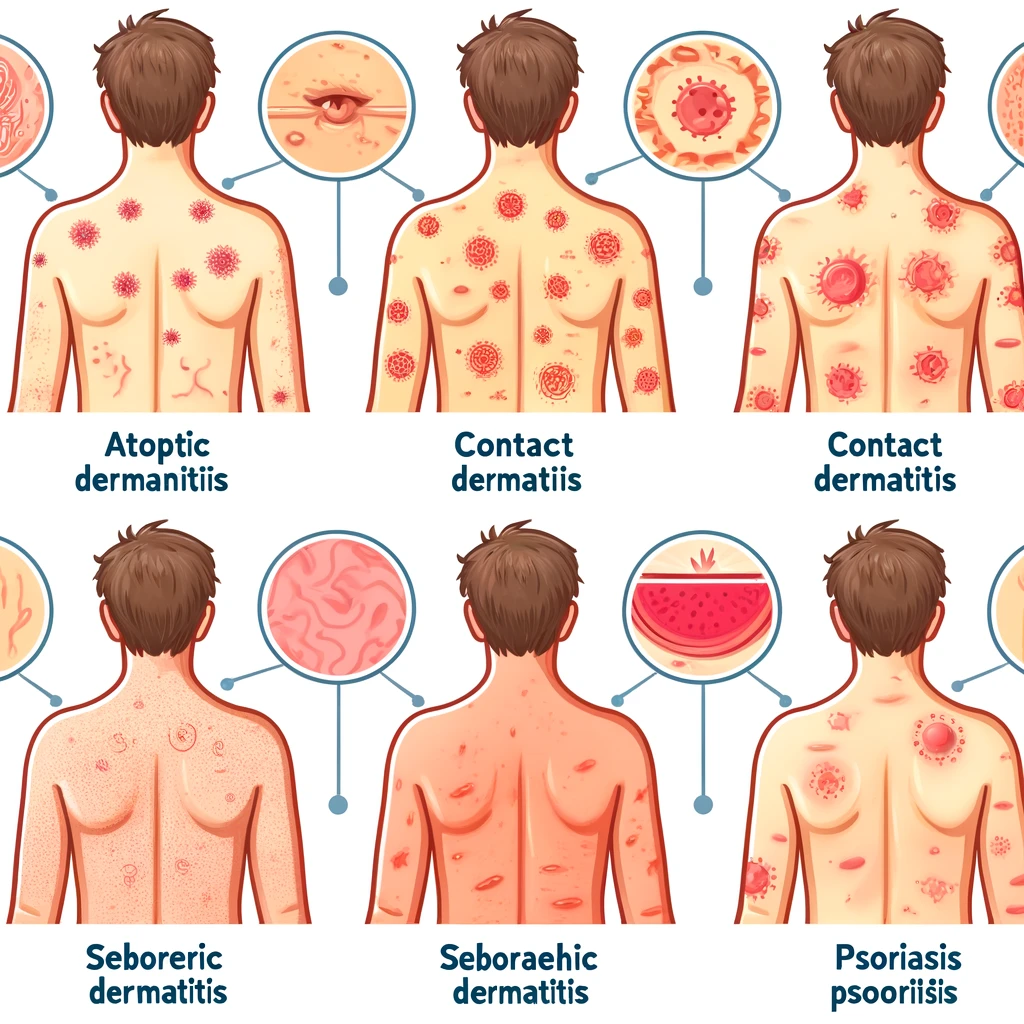
Rashes can be categorized based on their appearance, cause, and location. Here are some common types:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often in the creases of elbows and knees.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by skin contact with irritants or allergens, resulting in red, itchy, and sometimes blistered skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Often affects the scalp, causing scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff.
- Psoriasis: A chronic condition that leads to thick, red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Heat Rash (Miliaria): Caused by blocked sweat ducts, leading to small, itchy bumps.
Common Causes
Understanding the cause of a rash is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some common causes:
- Allergens: Such as pollen, pet dander, certain foods, or insect stings.
- Irritants: Including soaps, detergents, or chemicals.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause various types of rashes.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus or psoriasis can cause chronic rashes.
- Medications: Certain drugs can cause allergic reactions leading to rashes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a rash involves a thorough examination of the skin and a review of medical history. Dermatologists may use various diagnostic tools such as:
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin is taken for laboratory analysis.
- Patch Testing: Identifies specific allergens causing contact dermatitis.
- Blood Tests: Can help identify underlying conditions like infections or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment Options
The treatment of rashes depends on their cause and severity. Here are some common treatments:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids or antihistamines can reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oral Medications: Antihistamines, antibiotics, or antifungal medications may be prescribed.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin hydrated can prevent and soothe certain types of rashes.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants can prevent recurrence.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of rashes:
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected area can reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oatmeal Baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal to a bath can soothe itchy and irritated skin.
- Aloe Vera: The gel from an aloe vera plant can help reduce redness and irritation.
When to See a Doctor
While many rashes can be managed at home, certain symptoms indicate a need for medical attention:
- Severe Pain or Discomfort: If the rash is extremely painful or uncomfortable.
- Infection: Signs of infection such as pus, yellow scabs, or increased redness.
- Widespread Rash: If the rash covers a large area of your body.
- Persistent Rash: If the rash does not improve with home treatment.
Conclusion
Rashes can be bothersome, but with proper understanding and treatment, most can be effectively managed. By identifying the type of rash, its cause, and using appropriate treatments, you can achieve relief and prevent recurrence. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.
Table 1: Common Types of Rashes and Their Characteristics
| Rash Type | Characteristics | Common Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Dry, itchy, inflamed skin | Elbows, knees, face |
| Contact Dermatitis | Red, itchy, blistered skin | Hands, face |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Scaly patches, red skin, dandruff | Scalp, face, chest |
| Psoriasis | Thick, red patches covered with silvery scales | Scalp, elbows, knees |
| Heat Rash | Small, itchy bumps | Neck, chest, groin |
Image 1: Examples of Different Types of Rashes
Video: Understanding Rashes and Their Treatment
How to Make Yourself Poop: Effective Methods and Tips
Introduction
Regular bowel movements are essential for maintaining good digestive health. However, constipation is a common issue that can cause discomfort and frustration. This article provides a comprehensive guide on natural methods and lifestyle changes to promote regular bowel movements, ensuring you can manage constipation effectively.
Understanding Constipation
Constipation is characterized by infrequent or difficult bowel movements. Common symptoms include:
- Infrequent Bowel Movements: Fewer than three bowel movements per week.
- Hard, Dry Stools: Stools that are difficult to pass.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Bloating, pain, or discomfort in the abdomen.
Causes of Constipation
Several factors can contribute to constipation, including:
- Diet: Low fiber intake and dehydration.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyle.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause constipation.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or hypothyroidism.
Natural Methods to Relieve Constipation
Here are some effective natural methods to help relieve constipation:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps soften the stool.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity stimulates bowel movements.
- Establish a Routine: Try to have bowel movements at the same time each day.
- Respond to Urges: Don’t ignore the urge to poop.
Table 2: High-Fiber Foods to Include in Your Diet
| Food Item | Fiber Content (per serving) |
|---|---|
| Lentils | 15.6 grams |
| Black Beans | 15 grams |
| Chia Seeds | 10 grams |
| Broccoli | 5.1 grams |
| Apples | 4.4 grams |
Over-the-Counter Remedies
If natural methods are not effective, over-the-counter remedies can help:
- Fiber Supplements: Such as psyllium husk or methylcellulose.
- Stool Softeners: Help add moisture to the stool.
- Laxatives: Stimulant laxatives or osmotic laxatives can provide short-term relief.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can help stimulate bowel movements:
- Prune Juice: Known for its natural laxative effect.
- Coffee: Caffeinated coffee can stimulate the muscles in your digestive system.
- Probiotics: Supplements or foods like yogurt can improve gut health.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical advice:
- Severe Pain: Severe abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Blood in Stool: Indication of a more serious condition.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Could be a sign of an underlying issue.
- Persistent Constipation: If constipation lasts more than three weeks.
Conclusion
Constipation is a common issue, but with the right approach, it can be managed effectively. By incorporating high-fiber foods, staying hydrated, and maintaining an active lifestyle, you can promote regular bowel movements. If natural methods are insufficient, over-the-counter remedies and medical advice can provide further relief. Remember, a healthy digestive system is key to overall well-being.
Image 2: High-Fiber Foods for Better Digestion
Video: Tips for Relieving Constipation
Note: Ensure to insert relevant images and YouTube video links in place of placeholders in the final document.