Understanding Lower Right Abdominal Pain: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Lower right abdominal pain can be a concerning symptom, often prompting individuals to seek medical attention. This guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into the potential causes, diagnostic processes, and treatment options for pain in the lower right abdomen.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Anatomy of the Lower Right Abdomen
- Common Causes of Lower Right Abdominal Pain
- Appendicitis
- Kidney Stones
- Hernias
- Ovarian Cysts
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Less Common Causes
- Diagnostic Methods
- Treatment Options
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Prevention Tips
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Pain in the lower right abdomen can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. Understanding the underlying causes and seeking timely medical intervention is crucial for effective management and relief.
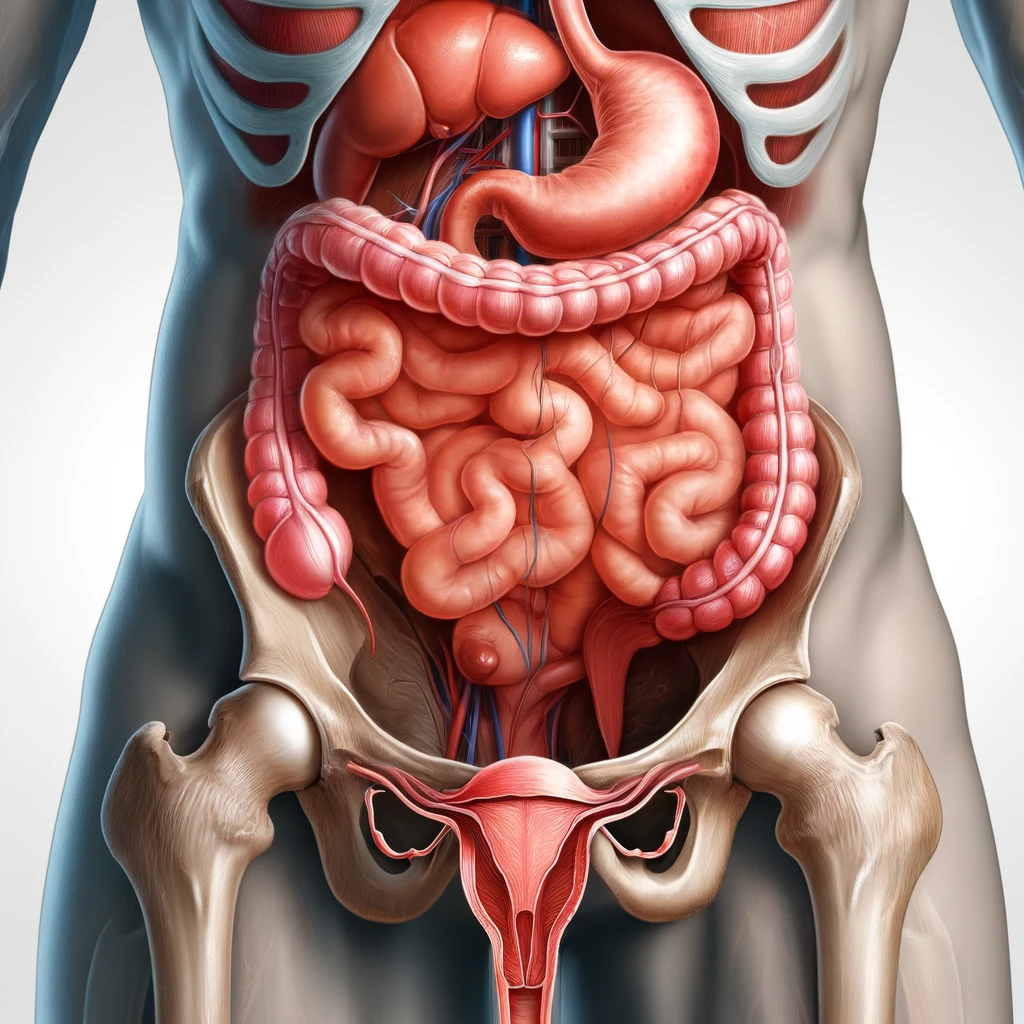
2. Anatomy of the Lower Right Abdomen
The lower right abdomen houses several vital structures, including:
- The appendix
- Part of the large intestine (cecum and ascending colon)
- Right ureter
- Reproductive organs in women (right ovary and fallopian tube)
- Blood vessels and nerves
3. Common Causes of Lower Right Abdominal Pain
Appendicitis
Description: Inflammation of the appendix, a small tube attached to the large intestine. Symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp pain beginning around the navel and shifting to the lower right abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination (tenderness in the lower right abdomen)
- Blood tests (elevated white blood cell count)
- Imaging (ultrasound or CT scan)
Treatment: Surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy).
Kidney Stones
Description: Hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the side and back, radiating to the lower abdomen and groin
- Painful urination
- Pink, red, or brown urine
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis:
- Urine test (to detect blood and minerals)
- Imaging (CT scan or ultrasound)
- Blood tests (to check kidney function)
Treatment:
- Pain relievers
- Drinking water to help pass the stone
- Medical procedures (extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy or surgery)
Hernias
Description: Protrusion of an organ through the wall of the cavity that normally contains it. Types:
- Inguinal hernia (most common)
- Femoral hernia
- Umbilical hernia
Symptoms:
- Bulge in the lower abdomen or groin
- Pain or discomfort, especially when bending over, coughing, or lifting
- Weakness or pressure in the groin
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination
- Imaging (ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI)
Treatment: Surgical repair of the hernia.
Ovarian Cysts
Description: Fluid-filled sacs within or on the surface of an ovary. Symptoms:
- Dull or sharp pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst
- Bloating or swelling
- Pain during bowel movements
- Pain during intercourse
Diagnosis:
- Pelvic examination
- Imaging (ultrasound)
- Blood tests (to rule out ovarian cancer)
Treatment:
- Watchful waiting (for small, asymptomatic cysts)
- Medications (hormonal contraceptives)
- Surgery (if the cyst is large or symptomatic)
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Conditions:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating and gas
- Weight loss
Diagnosis:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood tests
- Stool tests
- Colonoscopy or endoscopy
Treatment:
- Dietary changes
- Medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics)
- Surgery (in severe cases)
4. Less Common Causes
Other potential causes of lower right abdominal pain include:
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, causing pain.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the womb, typically in a fallopian tube.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches that can form in the intestines.
5. Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
Physical Examination
- Checking for tenderness, swelling, or masses in the abdomen.
Blood Tests
- Identifying infections, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
Imaging
- Ultrasound: Often used to examine organs and structures within the abdomen.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the abdominal organs.
- MRI: Used for more detailed imaging, particularly of soft tissues.
Other Tests
- Urine Tests: To detect infections or kidney stones.
- Endoscopy or Colonoscopy: To view the inside of the digestive tract.
6. Treatment Options
Medication
- Pain Relievers: To manage pain and discomfort.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: For conditions like IBS and Crohn’s disease.
Surgical Procedures
- Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix.
- Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder.
- Hernia Repair: To fix hernias.
- Cyst Removal: For problematic ovarian cysts.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Dietary Changes: For gastrointestinal disorders.
- Hydration: To help pass kidney stones.
- Rest and Relaxation: For mild cases of muscle strain or minor infections.
7. When to Seek Medical Help
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Severe, sudden abdominal pain
- Pain accompanied by fever, nausea, or vomiting
- Difficulty passing stools or gas
- Blood in stools or urine
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few hours
8. Prevention Tips
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber to prevent gastrointestinal issues.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to avoid kidney stones.
- Exercise Regularly: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of hernias.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular medical examinations can help detect issues early.
9. Conclusion
Lower right abdominal pain can stem from various causes, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the potential reasons and seeking prompt medical attention can lead to effective treatment and relief. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and being aware of the warning signs can also play a significant role in preventing abdominal pain.
References
Embedded YouTube Video
Tables and Charts
Table 1: Common Causes of Lower Right Abdominal Pain
| Cause | Description | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appendicitis | Inflammation of the appendix | Sharp pain, nausea, fever | Surgical removal |
| Kidney Stones | Mineral deposits in the kidneys | Severe pain, blood in urine, nausea | Pain relievers, hydration, surgery |
| Hernias | Protrusion of an organ through the abdominal wall | Bulge, discomfort, weakness | Surgical repair |
| Ovarian Cysts | Fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries | Abdominal pain, bloating, pain during intercourse | Observation, medication, surgery |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | Conditions like IBS, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss | Dietary changes, medication, surgery |
Table 2: Diagnostic Methods
| Method | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Checking for tenderness and masses in the abdomen | Initial assessment |
| Blood Tests | Identifying infections and inflammation | To diagnose infections, kidney function issues |
| Ultrasound | Imaging of abdominal organs | To examine organs, detect cysts or stones |
| CT Scan | Detailed imaging of abdominal structures | To provide a comprehensive view of abdominal organs |
| MRI | Detailed imaging of soft tissues | To provide detailed images of soft tissues, detect abnormalities |
| Urine Tests | Analysis of urine samples | To detect infections, kidney stones, and other urinary issues |
| Endoscopy/Colonoscopy | Direct visualization of the digestive tract | To diagnose gastrointestinal disorders |
Table 3: Treatment Options for Lower Right Abdominal Pain
| Treatment | Description | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Relievers | Medications to alleviate pain | General abdominal pain, kidney stones, hernias |
| Antibiotics | Medications to treat bacterial infections | Appendicitis, certain gastrointestinal disorders |
| Anti-inflammatory Drugs | Medications to reduce inflammation | IBS, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis |
| Appendectomy | Surgical removal of the appendix | Appendicitis |
| Cholecystectomy | Surgical removal of the gallbladder | Gallstones, gallbladder inflammation |
| Hernia Repair | Surgical procedure to fix hernias | Hernias |
| Cyst Removal | Surgical removal of ovarian cysts | Symptomatic or large ovarian cysts |
| Dietary Changes | Adjustments in diet to manage symptoms | IBS, Crohn’s disease, kidney stones |
| Hydration | Increased fluid intake to aid in passing stones | Kidney stones |
| Rest and Relaxation | Non-medical approaches to alleviate mild symptoms | Minor muscle strain, mild infections |
6. Treatment Options (Continued)
Appendectomy
Procedure: Surgical removal of the appendix. Indications: Appendicitis. Recovery: Most patients recover within a few weeks, but full recovery may take longer depending on the individual and surgical approach (laparoscopic vs. open surgery).
Cholecystectomy
Procedure: Surgical removal of the gallbladder. Indications: Gallstones, gallbladder inflammation. Recovery: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy typically allows for a quicker recovery compared to open surgery, with most patients resuming normal activities within a week.
Hernia Repair
Procedure: Surgical repair of hernias, which may involve pushing the protruding organ back into place and reinforcing the abdominal wall with mesh. Indications: Hernias. Recovery: Recovery time varies depending on the type of hernia and surgical approach, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Cyst Removal
Procedure: Surgical removal of ovarian cysts. Indications: Symptomatic or large ovarian cysts. Recovery: Recovery time depends on the size and type of cyst and the surgical approach, but most patients can resume normal activities within a few weeks.
7. When to Seek Medical Help
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Severe, Sudden Abdominal Pain
Severe, sudden pain that does not improve with rest or over-the-counter pain relievers may indicate a serious condition such as appendicitis or kidney stones.
Pain Accompanied by Fever, Nausea, or Vomiting
These symptoms may suggest an infection or inflammation that requires medical treatment.
Difficulty Passing Stools or Gas
Inability to pass stools or gas, especially if accompanied by abdominal distension, may indicate a bowel obstruction.
Blood in Stools or Urine
Blood in stools or urine may indicate an infection, inflammation, or other serious conditions that require immediate medical attention.
Persistent Pain Lasting More Than a Few Hours
Pain that persists for more than a few hours, especially if it worsens, should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
8. Prevention Tips
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fiber can help prevent gastrointestinal issues and maintain overall health. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps prevent kidney stones and supports overall bodily functions. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of hernias. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Routine Check-ups
Regular medical examinations can help detect issues early and prevent complications. Schedule annual check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Avoid Heavy Lifting
Avoid lifting heavy objects, or use proper lifting techniques to reduce the risk of hernias and muscle strain.
9. Conclusion
Lower right abdominal pain can result from a variety of conditions, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the potential causes and seeking timely medical intervention is crucial for effective management and relief. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and being aware of warning signs can also play a significant role in preventing abdominal pain.
By following the prevention tips and knowing when to seek medical help, you can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate lower right abdominal pain. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
References
Embedded YouTube Video
This article provides a thorough understanding of lower right abdominal pain, including common and less common causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of seeking medical help when necessary and offers practical prevention tips to maintain abdominal health.